ART 208.01 Introduction to Sculpture / Metal
Working Worksheet
Welding
Arc welding is a fusion processes for joining metals. By applying intense heat, two pieces of metal (termed the ‘parent’ metals) are melted and caused to intermix with intermediate molten filler metal (i.e. the welding wire termed the ‘work electrode’). To promote this fluid intermixing of molten metals, a gas shield is required to protect the molten metals from oxidation (exposure to air) and other chemical contaminations. Thus any arc welding function can be understood to combine three basic elements: Heat, Metal, and Flux.
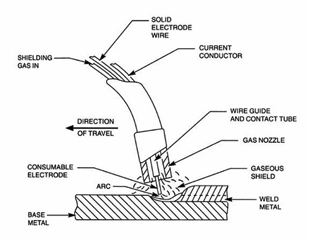
Heat: Electric
Melting of the Metals
What distinguishes MIG welding from other types of welding?
What causes the heat that melts both parent and electrode metals?
When do you know you need more heat? less heat?
How does one increase the heat of a weld?
Ground Electrode: What is its function? How should it be attached? What is the indication that it is incorrectly attached?
Metal: Running Good
Weld Beads

What does a good weld bead look like?
If your weld is too narrow and skinny what is the solution?
What is the most common cause of lumpy, non- continuous welds? What is the solution?
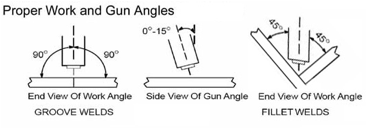
What is the proper position of the MIG gun?
How far should the welding wire stick out from the welding gun tip?
The wire feed isn’t working. What are two likely causes?
How should parent metal parts be prepared for joining?
Flux: Effective Gas
Shielding
How can you tell that the fluxing function is not working correctly?
What are three likely reasons for gas shield problems?
1.
2.
3.
Arc Welding Safety
Correct safety apparel includes:
What happens if you do not correctly protect your eyes?
Why is it so easy to burn yourself when handling hot metals?
Brazing:
How does brazing differ from arc welding?
Are the protective goggles the same used for arc welding? If so, how do they differ?
Why does a brazing torch use both oxygen and acetylene gases combined? (What function does each gas serve?)
What are the correct pressure settings for these two gases?
Oxygen: (psi)
Acetylene: (psi)
What are the steps to turning on the brazing torch?
1.
2.
3.
What are the steps to turning off the brazing torch?
1.
2.
3.
What is key to creating an effective brazed joint between metal rods?
Metal Fabrication
(including Cutting, Grinding, Drilling)
Why are there so many sparks when you cut and grind steel but nit when you cut and grind copper or aluminum?
What is a metal burr? Why is it dangerous?
What is required when drilling a hole in steel?
Name the three primary safety procedures for metal fabrication
1.
2.
3.
Sheet Metal
Fabrication: including snipping, bending (by hand, by heat, by roller), riveting
What are the two types of metal snips?
Name three causes of jagged cuts:
1.
2.
3.
When does one use a sheet metal rivet and when does one use a sheet metal screw?
What is the key to bending wire evenly?