ART 208.01 Introduction to Sculpture / Carpentry
Worksheet
|
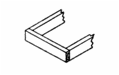
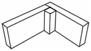
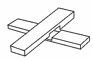
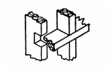
Know your Joints: |
||
|
|
|
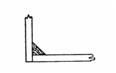
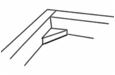
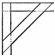
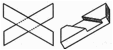
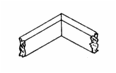
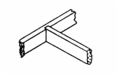
Examples
of triangulation to reinforce
joints |
|
|
|
|
|
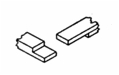
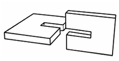
Spliced Joint
(w/recess cut) used where the ends
of two pieces are to be joined together in a continuous line to obtain extra
length. |
|
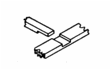
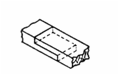
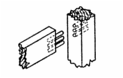
Dowel Joints: Joints secured by a small wooden peg
called a dowel. Used for single point attachments (w/ glue) or 2-sided blind
attachments. |
|
|
|
|
|
Joinery
Steps: # 1 Cutting Define these four cut types: á
Cross cut (square and miter) á
Rip cut á
Recess cut á
Notch cut á
Scroll cut Table Saw: What types of cuts are best made on
the table saw? Which guide/ fence are used for
which cuts? Wood kickback is the most common
danger on a table saw. When/why does it occur? How do you avoid it? Name three safety features on our
table saw. 1. 2. 3. Chop/ Miter Saw: What type(s) of cuts are best made
on the chop saw? What is the correct way to secure
the wood when making a cut? Band Saw: What two types of cuts are best
made on the band saw? 1. 2. What type of cuts should not be
made on the band saw? What is correct position of the
blade guide?
Joinery
Steps: # 2 Assembly What are the pros and cons of the
following fasteners (i.e., when do you them and when do you not use them?) á
Nails á
Brads á
Screws á
Machine screws/bolts á
Air nails What is pilot hole? What is its
purpose? How do you correctly size it? What is countersinking? What is its
purpose? What is the most common error when countersinking? When should you use glue and when
should you not use glue? Name some ways to ensure that a
right angle joint is assembled to be perfectly square? Joinery
Steps: # 3 Finishing (including filling, sanding, painting) When spackling a screw hole name 3
things you can do to ensure a flat smooth result. 1. 2. 3. Which sand paper is coarser 60 grit
or 120 grit? What is the main cause of a drippy
sloppy paint job? |